National Current Affairs – UPSC/IAS Exams- 1st October 2019
Niti Aayog School Education Quality Index
Topic: Reports and Indices
In News: NITI Ayog released the first edition of SEQI recently.
Highlights of the Report:
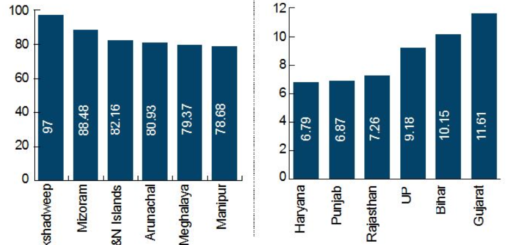
- There are huge differences in the quality of school education across the country, according to a Niti Aayog ranking released on Monday. Among 20 large States, Kerala was the best performer with a score of 76.6%, while Uttar Pradesh came in last with a score of 36.4%.
- Haryana, Assam and Uttar Pradesh showed the most improvement in their performance in 2016-17, in comparison to the base year of 2015-16.
- Tamil Nadu was the top performer in access and equity outcomes, while Karnataka led in learning outcomes. Haryana had the best infrastructure and facilities.
- Among smaller States, Manipur emerged as the best performer, while Chandigarh topped the list of Union Territories. West Bengal refused to participate in the evaluation process and has not been included in the rankings.
About SEQI:
- SEQI was developed by NITI Aayog to evaluate the performance of States and UTs in the school education sector.
- It is developed through a collaborative process, including key stakeholders such as Ministry of HRD, the World Bank and sector experts.
- Survey data, self-reported data from States and third-party verification is used in deriving the index.
- The index aims to bring an ‘outcomes’ focus to education policy by providing States and UTs with a platform to identify their strengths and weaknesses and undertake requisite course corrections or policy interventions.
Key indicators:
- The index consists of 30 critical indicators that assess the delivery of quality education. These indicators are categorized as below:
- Category 1: Outcomes: Learning outcomes, Access outcomes, Infrastructure and facilities for outcomes, Equity outcomes
- Category 2: Governance processes aiding outcomes
Model Mains Question: Neglect of primary health care and education in India are reasons for its backwardness, Comment.
Source: Hindu
Core Sectors of Economy
Topic: Economy
In News: Growth in the eight core sectors in August slumped to the lowest in four years and four months. The -0.5% registered in August 2019 was the lowest since April 2015.
More on the Topic:
- Growth in five out of the eight sectors of the Index of Eight Core Industries fell into the negative zone in August. The index had registered a growth of 2.7% in July 2019 and a robust 4.72% in August 2018.
- It is an indication of a continuing slowdown and weak demand in the system. The core sectors reflect demand from the power and infrastructure sectors, where the government’s own demand is important and public sector spending has been low in the last 3-4 months.
- This also shows that the economic slowdown is continuing and signs of a revival are not visible.
About Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI):
- It is monthly production volume index considered as lead indicator of monthly industrial performance.
- It measures collective and individual performance of production in selected eight core industries viz. Natural Gas(Weightage:6.88%), Coal(10.33%), Crude Oil(8.98%), Fertilizers(2.63%), Petroleum Refinery Products(28.04%), Steel(17.92%), Cement(5.37%) and Electricity(19.85%).
- It is compiled and released by Office of Economic Adviser (OEA), Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP), Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The eight infrastructure sectors, constitute 40.27% of total index of industrial production (IIP). These eight core industries have impact on general economic activities as well as industrial activities. (Base year for ICI is 2011-12).
‘Ancient river’ discovered in Uttar Pradesh
Topic: Environment and Ecology
In News: The Union Water Ministry has excavated an old, dried-up river in Prayagraj (formerly Allahabad) that linked the Ganga and Yamuna rivers.
More on the Topic:
- The “ancient buried river” is around 4 km wide, 45 km long and consisted of a 15-metre-thick layer buried under soil.
- The discovery was made by a team of scientists from the CSIR-NGRI (National Geophysical Research Institute) and the Central Groundwater Board during a helicopter-borne geophysical survey covering the Prayagraj and Kaushambi region in Uttar Pradesh.
- Knowledge on subsurface connectivity between Ganga and Yamuna rivers will play a very crucial role in planning of Ganga cleaning and protecting safe groundwater resources.
Source: Hindu
Ban on export of onion
Topic: Economy
In News: In a bid to tame onion prices, which have doubled in the domestic retail market since July, the government has banned exports of all varieties of onion and imposed stock limits on onion traders to facilitate release of stocks and prevent hoarding by traders.
More on the Topic:
- In this regard, Commerce and industry ministry amended the export policy of onion, making it ‘prohibited’ from ‘free’ earlier.
- Retail traders across the country will now be able to stock only up to 100 quintals of onion while wholesale traders will be allowed to stock up to 500 quintals.
- Various experts stated that the ban is an irrational, and sub-optimal solution. Instead, efforts should be channelized into investing in scientific storage and processing facilities that will help augment supplies during a crisis.
- There is a need to promote modern cold storages and develop a system similar to that of the warehouse receipt system for farmers and onion dehydrating units should be set up and promote demand for dehydrated onions amongst large consumers.
Source: The Hindu
Industry 4.0
Topic: Economy
In News: Recently, a pilot project was launched to usher in ‘Industry 4.0’ in India under the aegis of ‘Technology Mission for Indian Railways’.
More on the Topic:
- The Ministry of Railways, Department of Science and Technology, and IIT Kanpur joined hands together to implement the project at the Modern Coach Factory (MCF), Raebareli in Uttar Pradesh.
Significance:
- Full transition to the digital factory using ‘Industry 4.0’ across entire value chain from design to production will help enhance productivity hugely by providing insight into production process to take the decisions in real time basis, minimizing human errors by effective monitoring to ensure that resources are put to the best utilization measured by, what is called the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
About Industry 4.0:
- Commonly referred to as the fourth industrial revolution, it is a name given to the current trend of automation, interconnectivity and data exchange in manufacturing technologies to increase productivity.
- Industry 4.0 is a complex Cyber-Physical Systems which synergizes production with digital technologies, the Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, Big Data & Analytics, Machine Learning and Cloud Computing.
The world has witnessed the following three industrial revolutions in the past:
- The first one occurred at the end of 18th century and the beginning of 19th century. It was characterised by mechanisation of simple manual tasks. Steam-powered engines, spinning jenny are the products of this wave.
- The second wave marked the early decades of 20th century and is characterised by introduction of steel and use of electricity in factories. While the first revolution had seen mechanisation of manual tasks, the second one saw increase in efficiency as well as mobility of factory machinery.
- The third industrial revolution started by 1950s. The definitive feature of this revolution is incorporation of more electronic and eventually computertechnology in the production process. A shift towards digital technology and automation software and away from analog and mechanical technology was observed.
Source: Hindu
Climate Vulnerability Map of India
Topic: Environment and Ecology
In News: For preparing communities and people to meet the challenge arising out of climate changes a pan India climate vulnerability assessment map is being developed under a joint project of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) under the Union Ministry of Science and Technology and Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
More on the Topic:
- A climate vulnerability atlas has already been developed for 12 states in the Indian Himalayan Region, using a common framework.
- This methodology will be extended to non-Himalayan states so that country can have a national level climate vulnerability profile for India. The atlas is expected to be ready by the middle of 2020.
Significance of Mapping Climate vulnerability:
- Using a common methodology for assessing vulnerability is critical for comparison and for planning adaptation strategies. It also helps in identifying what makes a state or district vulnerable to climate change.
- Climate risk is interplay of hazard, exposure and vulnerability. There is a rise in climate-sensitive livelihood of people. While the occurrence of natural hazards such as landslides, droughts and floods is projected to go up, their impact depends on the level of exposure such as presence of people and infrastructure in areas. Hence a common methodology for assessing vulnerability is critical for comparison and for planning adaptation strategies.
- The vulnerability assessments will be useful for officials, decision makers, funding agencies and experts to have a common understanding on vulnerability and enable them to plan for adaptation.
Source: Hindu
Penicillin
Topic: Health
In News: In a bid to fight drug resistance and tackle the prevalence of rheumatic heart disease, the Government of India is planning a revival of the drug named Penicillin.
More on the Topic:
- India has a high burden of rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease (which generally goes undiagnosed and leads to many maternal deaths at the time of childbirth).
- Rheumatic fever is endemic in India and remains one of the major causes of cardiovascular disease, accounting for nearly 25-45% of acquired heart disease.
- Penicillin is the cheapest option for rheumatic fever treatment.
- Penicillin was the first antibiotic that was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming.
- It is still the first-line antibiotic drug in many western countries.
- In India, it gradually went out of the markets because of unrealistic price control measures of the government.
- The prices of the drug were kept so low that the manufacturers stopped making the drug and Penicillin went out of production. Although some of its more expensive derivatives continued to be prescribed.
Source: PIB