Ministry of Agriculture Schemes
1. Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana

- In April, 2016, the government of India had launched Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) after rolling back the earlier insurance schemes viz. National Agriculture Insurance Scheme (NAIS), Weather-based Crop Insurance scheme and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- Premium: It envisages a uniform premium of only 2% to be paid by farmers for Kharif crops, and 1.5% for Rabi crops. The premium for annual commercial and horticultural crops will be 5%.
- The scheme is mandatory for farmers who have taken institutional loans from banks. It’s optional for farmers who have not taken institutional credit.
Objectives
- Providing financial support to farmers suffering crop loss/damage arising out of unforeseen events.
- Stabilizing the income of farmers to ensure their continuance in farming.
- Encouraging farmers to adopt innovative and modern agricultural practices.
- Ensuring flow of credit to the agriculture sector which contributes to food security, crop diversification and enhancing growth and competitiveness of agriculture sector besides protecting farmers from production risks.
2. National Agriculture Market (NAM)

- The National Agriculture Market (NAM) is a pan-India electronic trading portal, which links the existing Agricultural Produce Market Committee (APMC) mandis across the country to form a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
- The NAM portal is a single window service for any information and services related to APMC that includes:
- Commodity arrivals and prices
- Buy and sell trade offers
- Provision to respond to trade offers, among other services
- The NAM reduces the transaction costs and information irregularity even when the agriculture produce continues to flow through the mandis.
- The states can administer agriculture marketing as per their agri-marketing regulations, under which, the State is divided into various market areas and each market area is administered by a separate APMC which will impose its own marketing regulation that include fees.
Objectives of NAM
- A nation-wide e-market portal for transparent sale and transactions and price discovery in the regulated markets.
- The States can promote the e-trading as per their APMC Act and enact suitable provision under the act by their State Agricultural Marketing Board/APMC.
- Liberal licensing of traders or buyers and commission agents by State authorities without any pre-condition of physical presence or possession of shop or premises in the market yard.
- One license for a trader valid across all markets in the State.
- Synchronisation of quality standards of agricultural commodities and facility for assessing (quality testing) infrastructure in every market to facilitate informed bidding by buyers.
- Single point tax of market fees on the first wholesale purchase from the farmer.
- Soil Testing Laboratories facility in/or near the particular mandi to help visiting farmers to access this provision in the mandi itself.
3. National Food Security Mission’ (NFSM)

- The National Development Council (NDC) launched National Food Security Mission on October 2007.
- The objectives was to increase the production of rice, wheat and pulses.The Mission is being continued during 12th Five Year Plan with new targets of additional production of food grains of 25 million tons of food grains
- The National Food Security Mission (NFSM) during the 12th Five Year Plan will had 5 components:
- (i) NFSM- Rice;
- (ii) NFSM-Wheat;
- (iii) NFSM-Pulses,
- (iv) NFSM-Coarse cereals and
- (v) NFSM-Commercial Crops.
- Based on past experience and performance of 12th Plan, the programme is being continued upto 2019-20, which is co-terminus with Fourteenth Finance Commission (FFC) period.
- The targets to achieve are 13 million tonnes of additional foodgrains production comprising of Rice – 5 million tonnes, Wheat- 3 million tonnes, Pulses- 3 million tonnes and Coarse Cereals- 2 million tonnes.
4.National Mission on Oilseeds and Oil Palm (NMOOP)

Palm fruit ready to be taken to the mill.
- National Mission on Oilseeds and Oil Palm (NMOOP) is under implementation since 2014-15 in 27 states including North-Eastern States for increasing production and productivity of oilseeds including area expansion of oil palm.
- Under both NFSM-pulses and NMOOP financial assistance is available for organizing cluster demonstration and Front Line Demonstration (FLD) of improved technologies, supply of quality seeds including seeds mini kits of new varieties, production inputs like soil ameliorants, micro nutrients, bio-fertilizers, plant protection chemicals including bio-agents, farm machineries, water saving devices and capacity building of farmers/extension workers to increase the production and productivity of the pulses and oilseeds.
National Food Security Mission Seed Village programme
- To upgrade the quality of farmer’s saved seeds financial assistance for distribution of foundation/certified seeds at 50% cost of the seeds for agricultural crops for half an acre per farmer was available up to the year 2013-14.
- From the year 2014-15, the financial assistance for distribution of foundation/certified seeds at 50% cost of the seeds for cereal crops and 60% for pulses, oilseeds, fodder and green manure crops for production of quality seeds is now available for one acre per farmer.
Certified Seed Production of Pulses, oilseeds, Fodder & Green Manure crops through Seed Village.
- In order to enhance certified seed production of Pulses, oilseeds, Fodder & Green manure crops in the country, this component has been initiated from 2014-15. Under this component the financial assistance for distribution of foundation seeds at 75% cost of the seeds for pulses, oilseeds, fodder and green manure crops for production of Certified Seeds is available for the farmers.
- The above schemes are demand driven and implemented by the States/implementing agencies for benefiting the farmers.
5. Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture

- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) has been launched for the holistic development of horticulture in the country since 2014 – 15. It subsumed six schemes of the Department of Agriculture and cooperation on horticulture development. Out of these six schemes three are centrally sponsored schemes they are National Horticultural Mission, Horticulture Mission for North east and Himalayas,National Bamboo Mission and the three Central sector schemes are National Horticulture Board,Coconut Development Board, and Central Institute of Horticulture, Nagaland.
- MIDH lays emphasis on enhancing horticulture production, augmenting farmers income and strengthening nutritional security. It plans to improve productivity by way of quality germ plasm, planting material and water use efficiency through micro irrigation.
National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM) is one of the sub schemes of Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) which is being implemented by State Horticulture Missions (SHM) in selected districts of 18 States and four Union Territories.
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM) was launched in 2005 – 06 as Centrally sponsored scheme to enhance the horticulture production and improver nutritional security and income support to farm households and others. It adopts area based regionally differentiated strategies.
- Horticulture Mission for North East and Himalayan States (HMNEH): is one of the sub schemes of Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) which is being implemented by State Horticulture Missions (SHM) in the North Eastern States and Himalayan States. The mission covers all North eastern states including Sikkim and three himalayan states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- National Bamboo Mission (NBM): is one of the sub schemes of Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) which is being implemented by State Bamboo Development Agencies (BDA)/ Forest Development Agency (FDA) in all the States and UTs.The Mission envisages promoting holistic growth of bamboo sector by adopting area-based, regionally differentiated strategy and to increase the area under bamboo cultivation and marketing.
- National Horticulture Board (NHB): was set up by Government of India in April 1984 on the basis of recommendations of the “Group on Perishable Agricultural Commodities”, headed by Dr M. S. Swaminathan, the then Member (Agriculture), Planning Commission, Government of India. The NHB is registered as a Society under the Societies Registration Act 1860, with its headquarters at Gurgaon.
- Coconut Development Board (CDB): is a statutory body established in 1981 under the Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India for the integrated development of coconut cultivation and industry in the country with focus on productivity increase and product diversification.
6. National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture
- National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture was launched in the year 2011 by Indian Council on Agricultural Research (ICAR) (an autonomous body responsible for coordinating agricultural education and research in India that reports to the Department of Agriculture and Research (DARE) in the Ministry of Agriculture and is presided over by the Union Minister of Agriculture).
- The initiative recognizes India s vulnerability to climate change with nearly half of its population dependent on agriculture. It is estimated that by 2039, climate change could cause a drop in production by 4 to 9 % which could, in turn, cost up to 1.5 % of GDP as Agriculture makes nearly 16% of India s GDP. To address this emerging challenge, NICRA was launched with the following objectives.
- Research to improve production and risk management so as to enhance climate resilience of Indian agriculture.
- Technology demonstration to enable vulnerable districts in coping with climate change through demonstration of site specific technologies on farmer s fields.
- Capacity building of scientists and other stakeholders in climate resilient research
Salient Features
- Assessment of Crop Zones and their Climate Vulnerability
- Measuring GHG emissions
- Screening of crop germplasm to promote drought resistant varieties
- Evaluation and adoption of new technologies of paddy cultivation
- Special attention to livestock and fishery sectors
- understanding of crop-pest/pathogen relationship under changing the climate
- Facilitating wider adoption by farmers through KVKs and NMSA
7. National Dairy Plan
- It is a Central Sector Scheme .Phase I is from 2011-12 to 2018-19
Objectives
- To help increase productivity of milch animals and thereby increase milk production to meet the rapidly growing demand for milk.
- To help provide rural milk producers with greater access to the organised milk-processing sector.
- It has three components:
- Productivity Enhancement,
- Village based milk procurement systems and
- Project Management and Learning
8. National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture

- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) has been formulated for enhancing agricultural productivity especially in rainfed areas focusing on integrated farming, water use efficiency, soil health management and synergizing resource conservation.
Objectives
- To make agriculture more productive, sustainable, remunerative and climate resilient by promoting location specific Integrated/Composite Farming Systems;
- To conserve natural resources through appropriate soil and moisture conservation measures;
- To adopt comprehensive soil health management practices based on soil fertility maps, soil test based application of macro & micro nutrients, judicious use of fertilizers etc.;
- To optimize utilization of water resources through efficient water management to expand coverage for achieving ‘more crop per drop’ ;
- To develop capacity of farmers & stakeholders, in conjunction with other on – going Missions e.g. National Mission on Agriculture Extension & Technology, National Food Security Mission, National Initiative for Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) etc., in the domain of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures;
- To pilot models in select blocks for improving productivity of rainfed farming by mainstreaming rainfed technologies refined through NICRA and by leveraging resources from other schemes/Missions like Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP), RKVY etc.; and
- To establish an effective inter and intra Departmental/Ministerial co – ordination for accomplishing key deliverables of National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture under the aegis of National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- MSA has following four (4) major programme components or activities:
- Rainfed Area Development (RAD): RAD adopts an area based approach for development and conservation of natural resources along with farming systems. This component has been formulated in a ‘watershed plus framework’, i.e., to explore potential utilization of natural resources base/assets available/created through watershed development and soil conservation activities /interventions under MGNREGS, NWDPRA, RVP&FPR, RKVY, IWMP etc.. This component introduces appropriate farming systems by integrating multiple components of agriculture such as crops, horticulture, livestock, fishery, forestry with agro based income generating activities and value addition. Besides, soil test/soil health card based nutrient management practices, farmland development, resource conservation and crop selection conducive to local agro climatic condition are also promoted under this component.
- On Farm Water Management (OFWM): OFWM focuses primarily on enhancing water use efficiency by promoting efficient on – farm water management technologies and equipment. This not only focuses on application efficiency but, in conjunction with RAD component, also will emphasize on effective harvesting & management of rainwater.
To conserve water on farm itself, farm ponds may be dug using MGNREGA funds and earth moving machinery (to the extent manual digging under MGNREGA is not feasible)
- Soil Health Management (SHM): SHM aims at promoting location as well as crop specific sustainable soil health management including residue management, organic farming practices by way of creating and linking soil fertility maps with macro – micro nutrient management, appropriate land use based on land capability, judicious application of fertilizers and minimizing the soil erosion/degradation.
- Assistance will be provided for various improved package of practices based on land use and soil characteristics, generated through geographical information system (GIS) based thematic maps and database on land and soil characteristics through extensive field level scientific surveys. Besides, this component will also provide support to reclamation of problem soils (acid/alkaline/saline). This component will be implemented by State Govt., National Centre of Organic Farming (NCOF), Central Fertilizer Quality Control & Training Institute (CFQC&TI) and Soil and Land Use Survey of India (SLUSI).
- Climate Change and Sustainable Agriculture: Monitoring, Modeling and Networking (CCSAMMN): Comprehensive pilot blocks will be supported to illustrate functional mechanism for dissemination of rainfed technologies, planning, convergence and coordination with flagship schemes/Missions like MGNREGS, IWMP, Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), RKVY, NFSM, NHM, NMAET etc. Such an integrated action of input and output flows across agriculture, livestock and other production systems will harness the growth potential of the rainfed production systems, imparting sustainability of local production systems while negotiating climate change risks.
9. Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana

Objective
- To achieve 4% annual growth in agriculture
- The scheme is launched to incentivize the states to increase their investment in Agriculture
- Scheme incentivize the States to provide additional resources in their State Plans over and above their baseline expenditure to bridge critical gaps.
- A state is eligible for funding under the RKVY if it maintains or increases the percentage of its expenditure on Agriculture and its Allied Sectors with respect to the total State Plan Expenditure year on year.
- It covers all sectors of agriculture like: (don’t remember them)
- Animal Husbandry
- Agri-Finance
- Agriculture Marketing etc.
Sub Schemes of RSBY are
- Bringing Green Revolution to Eastern Region : To improve rice based cropping system in eastern India.
- Initiative on Vegetable Clusters : To increase production of vegetables
- National Mission for Protein Supplements
- Saffron Mission : Started in 2010-11; To improve saffron cultivation in JK
- Vidharbha Intensive Irrigation Development Programme
- Crop Diversification
- Framework:
- Under this scheme, the central government provides support to states on the basis of their own budget on Agriculture & Allied Sectors. The states are mandatorily required to prepare the District and State Agriculture Plans that comprehensively cover resources and indicate definite action plans.
10. Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna
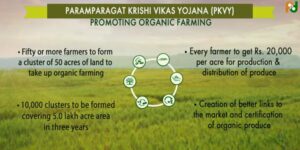
- “Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana” is an elaborated component of Soil Health Management (SHM) of major project National Mission of Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA). Under PKVY Organic farming is promoted through adoption of organic village by cluster approach and PGS certification.
The Scheme envisages
- Promotion of commercial organic production through certified organic farming.
- The produce will be pesticide residue free and will contribute to improve the health of consumer.
- It will raise farmer’s income and create potential market for traders.
- It will motivate the farmers for natural resource mobilization for input production.
Programme implementation
- Groups of farmers would be motivated to take up organic farming under Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
- Fifty or more farmers will form a cluster having 50 acre land to take up the organic farming under the scheme. In this way during three years 10,000 clusters will be formed covering 5.0 lakh acre area under organic farming.
- There will be no liability on the farmers for expenditure on certification.
- Every farmer will be provided 20,000 per acre in three years for seed to harvesting of crops and to transport produce to the market.
- Organic farming will be promoted by using traditional resources and the organic products will be linked with the market.
- It will increase domestic production and certification of organic produce by involving farmers
11. Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana

- The overreaching vision of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) is to ensure access to some means of protective irrigation to all agricultural farms in the country, to produce ‘per drop more crop’, thus bringing much desired rural prosperity.
Objectives
- Achieve convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level (preparation of district level and, if required, sub district level water use plans).
- Enhance the physical access of water on the farm and expand cultivable area under assured irrigation (Har Khet ko pani).
- Integration of water source, distribution and its efficient use, to make best use of water through appropriate technologies and practices.
- Improve on – farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage and increase availability both in duration and extent.
- Enhance the adoption of precision – irrigation and other water saving technologies (More crop per drop).
- Enhance recharge of aquifers and introduce sustainable water conservation practices.
- Ensure the integrated development of rainfed areas using the watershed approach towards soil and water conservation, regeneration of ground water, arresting runoff, providing livelihood options and other NRM activities.
- Promote extension activities relating to water harvesting, water management and crop alignment for farmers and grass root level field functionaries.
- Explore the feasibility of reusing treated municipal waste water for peri – urban agriculture.
- Attract greater private investments in irrigation.
PMKSY has the following programme components
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP): To focus on faster completion of ongoing Major and Medium Irrigation including National Projects.
PMKSY (Per Drop More Crop)
- Programme management, preparation of State/District Irrigation Plan, approval of annual action plan, Monitoring etc.
- Promoting efficient water conveyance and precision water application devices like drips, sprinklers, pivots, rain – guns in the farm (Jal Sinchan);
- Construction of micro irrigation structures to supplement source creation activities including tube wells and dug wells
PMKSY (Watershed Development)
- Effective management of runoff water and improved soil & moisture conservation activities such as ridge area treatment, drainage line 5 treatment, rain water harvesting, in – situ moisture conservation and other allied activities o n watershed basis.
- Converging with MGNREGS for creation of water source to full potential in identified backward rainfed blocks including renovation of traditional water bodies
12. Soil Health Card Scheme

- ‘Soil Health Card’ Scheme has been introduced to assist State Governments to issue soil health cards to all farmers in the country.
- It is a Government of India’s scheme promoted by the Department of Agriculture & Co-operation under the Ministry of Agriculture.
- It will be implemented through the Department of Agriculture of all the State and Union Territory Governments.
- A SHC is meant to give each farmer soil nutrient status of his holding and advice him on the dosage of fertilizers and also the needed soil amendments, that he should apply to maintain soil health in the long run.
- It is likely to develop an application software for the States for online generation of soil health cards and fertilizer recommendations. Dissemination of soil testing results through SMSs is enabled.
Objectives
- To issue soil health cards every 3 years, to all farmers of the country, so as to provide a basis to address nutrient deficiencies in fertilization practices.
- To strengthen functioning of Soil Testing Laboratories (STLs) through capacity building, involvement of agriculture students and effective linkage with Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) / State Agricultural Universities (SAUs).
- To diagnose soil fertility related constraints with standardized procedures for sampling uniformly across states and analysis and design taluqa / block level fertilizer recommendations in various district.
- To develop and promote soil test based nutrient management in the districts for enhancing nutrient use efficiency.
- To build capacities of district and state level staff and of progressive farmers for promotion of nutrient management practices.
13. Minimum Support Price
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is a form of market intervention by the Government of India to insure agricultural producers against any sharp fall in farm prices.
- The minimum support prices are announced by the Government of India at the beginning of the sowing season for certain crops on the basis of the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- MSP is price fixed by Government of India to protect the producer – farmers – against excessive fall in price during bumper production years.
- The minimum support prices are a guarantee price for their produce from the Government. The major objectives are to support the farmers from distress sales and to procure food grains for public distribution.
- In case the market price for the commodity falls below the announced minimum price due to bumper production and glut in the market, government agencies purchase the entire quantity offered by the farmers at the announced minimum price.
- Government announces minimum support prices (MSPs) for 22 mandated crops and fair and remunerative price (FRP) for sugarcane. In addition, the MSPs of toria and de-husked coconut are fixed on the basis of the MSPs of rapeseed/mustard and copra, respectively. The list of crops are as follows.
- Cereals (7) – paddy, wheat, barley, jowar, bajra, maize and ragi
- Pulses (5) – gram, arhar/tur, moong, urad and lentil
- Oilseeds (8) – groundnut, rapeseed/mustard, toria, soyabean, sunflower seed, sesamum, safflower seed and nigerseed
- Raw cotton,Raw jute,Copra,De-husked coconut,Sugarcane (Fair and remunerative price),Virginia flu cured (VFC) tobacco
14. Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) is a price support mechanism implemented on the request of State Governments for procurement of perishable and horticultural commodities in the event of a fall in market prices. The Scheme is implemented when there is at least 10% increase in production or 10% decrease in the ruling rates over the previous normal year.
- Market Intervention Scheme works in a similar fashion to Minimum Support Price based procurement mechanism for food grains, but is an adhoc mechanism.
- Its objective is to protect the growers of these horticultural/agricultural commodities from making distress sale in the event of bumper crop during the peak arrival period when prices fall to very low level. Thus it provides remunerative prices to the farmers in case of glut in production and fall in prices.
- The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation is implementing the scheme. Under MIS, funds are not allocated to the States. Instead, central share of losses as per the guidelines of MIS is released to the State Governments/UTs, for which MIS has been approved, based on specific proposals received from them.
- Under the Scheme, in accordance with MIS guidelines, a pre-determined quantity at a fixed Market Intervention Price (MIP) is procured by NAFED as the Central agency and the agencies designated by the state government for a fixed period or till the prices are stabilized above the MIP whichever is earlier. The area of operation is restricted to the concerned state only.
- The MIS has been implemented in case of commodities like apples, kinnoo/malta, garlic, oranges, galgal, grapes, mushrooms, clove, black pepper, pineapple, ginger, red-chillies, coriander seed, isabgol, chicory, onions, potatoes, cabbage, mustard seed, castor seed, copra, palm oil etc. in the States of Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Maharshtra, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Kerala, Jammu and Kashmir, Mizoram, Sikkim, Meghalaya, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Andaman and Nicobar islands, Lakshadweep etc.














