Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change
National Action Plan on Climate Change
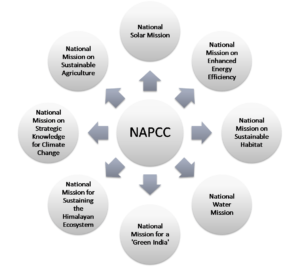
- The action plan outlines a number of steps to simultaneously advance India’s development and climate change-related objectives.
- National Solar Mission: The NAPCC aims to promote the development and use of solar energy for power generation and other uses, with the ultimate objective of making solar competitive with fossil-based energy options
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency: The NAPCC recommends mandating specific energy consumption decreases in large energy-consuming industries, with a system for companies to trade energy-saving certificates, financing for public–private partnerships to reduce energy consumption through demand-side management programs in the municipal, buildings, and agricultural sectors, and energy incentives, including reduced taxes on energy-efficient appliances.
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat: The NAPCC also aims at promoting energy efficiency as a core component of urban planning by extending the existing Energy Conservation Building Code, strengthening the enforcement of automotive fuel economy standards, and using pricing measures to encourage the purchase of efficient vehicles and incentives for the use of public transportation. The NAPCC also emphasizes on waste management and recycling.
- National Water Mission: The NAPCC sets a goal of a 20% improvement in water use efficiency through pricing and other measures to deal with water scarcity as a result of climate change.
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem: This particular mission sets the goal to prevent melting of the Himalayan glaciers and to protect biodiversity in the Himalayan region.
- Green India Mission: The NAPCC also aims at afforestation of 6 million hectares of degraded forest lands and expanding forest cover from 23 to 33% of India’s territory.
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture: The NAPCC aims to support climate adaptation in agriculture through the development of climate-resilient crops, expansion of weather insurance mechanisms, and agricultural practices.
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change: To gain a better understanding of climate science, impacts, and challenges, the plan envisions a new Climate Science Research Fund, improved climate modeling, and increased international collaboration. It also encourages private sector initiatives to develop adaptation and mitigation technologies through venture capital funds.
Secure Himalaya Project

- Objective of the mission is to ensure conservation of locally and globally significant biodiversity, land and forest resources in high Himalayan ecosystem spread over four states of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarkhand and Sikkim.
Features:
- It is launched by MoEFCC in association with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- The project is 6 years long and is meant for specific landscapes including Changthang (Jammu and Kasmir), Lahaul – Pangi and Kinnaur (Himachal Pradesh), Gangotri – Govind and Darma – Byans Valley in Pithoragarh (Uttarakhand) and Kanchenjunga – Upper Teesta Valley (Sikkim).
- The project includes protection of snow leopard and other endangered species and their habitats and also securing livelihoods of people in region and enhancing enforcement to reduce wildlife crime.
- Under it, enhanced enforcement efforts and monitoring will be undertaken to curb illegal trade in some medicinal and aromatic plants which are among most threatened species in these landscapes.
India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP)

- The thrust of the India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) is to look for synergies in actions for securing both environmental and socio-economic benefits.
The India Cooling Action seeks to
- Reduce cooling demand across sectors by 20% to 25% by 2037-38
- Reduce refrigerant demand by 25% to 30% by 2037-38
- Reduce cooling energy requirements by 25% to 40% by 2037-38
- Recognize “cooling and related areas” as a thrust area of research under the national S&T Programme
- Training and certification of 100,000 servicing sector technicians by 2022-23, synergizing with Skill India Mission. These actions will have significant climate benefits.
The following benefits would accrue to society over and above the environmental benefits:
- Thermal comfort for all – provision for cooling for EWS and LIG housing
- Sustainable cooling – low GHG emissions related to cooling
- Doubling Farmers Income – better cold chain infrastructure – better value of products to farmers, less wastage of produce
- Skilled workforce for better livelihoods and environmental protection
- Make in India – domestic manufacturing of air-conditioning and related cooling equipment’s
- Robust R&D on alternative cooling technologies – to provide the push to innovation in a cooling sector
Climate Resilience Building among Farmers through Crop Residue Management

- It is a regional project approved by National Steering Committee on Climate Change (MoEFCC) under NAFCC
- The project aims to mitigate climate change impacts and enhance adaptive capacity and also to counter the adverse environmental impacts that arise from stubble burning.
- The project will be implemented following a phased approach. The first phase of the project has been approved at a cost of approximately Rs. 100 Crore for the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Awareness generation and capacity building activities will be undertaken to encourage farmers to adopt alternate practices which would also help diversify livelihood options and enhance farmer’s income.
- Technological interventions will be undertaken for timely management of crop residue in addition to effective utilisation of existing machineries. Implementable and sustainable entrepreneurship models will be created in rural areas through upscaling successful initiatives and innovative ideas.
- Based upon the performance in the first phase, the scope could be enhanced and more activities can be supported subsequently.
Objectives of the Project:
To lower Green House Gases Emissions in project areas by
- Creating awareness among farmers through crop residue management and by Promoting alternate uses of crop residue.
- To create implementable and sustainable entrepreneurship models in rural areas by engaging FCs/ FPOs /PACs/ JLGs/ Individual entrepreneurs for effective crop residue management through upscaling successful initiatives and innovative ideas.
- To enhance the climate resilience and income of the farmers through alternative uses of crop residue management in project areas.
- To identify the other co-benefits and suggest policy intervention
Ministry of Earth Sciences
National Monsoon Mission
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune will coordinate and lead the effort for improving the forecasts on seasonal and intra seasonal scale.
- National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF), Noida will lead and coordinate the efforts for improving the forecasts in the medium range scale up to week two forecasts. These will be made operational by the India Meteorological Department (IMD), New Delhi
Objectives:
- To improve Seasonal and Intra-seasonal Monsoon Forecast
- To improve Medium Range Forecast.
- To develop a state of the art dynamical prediction system for monsoon rainfall on all different time scales i.e. from short-range to seasonal.
Features:
- For Long range forecasting (upto a season), American model called Climate Forecast System (CFS) is used, which is a coupled-Ocean forecasting system i.e. it combines data from ocean, atmosphere and land.
- For short to medium range (upto 20 days) Unified Model (UM) developed by UK is used.
- In its phase I, IMD was able to develop high resolution-coupled dynamical prediction system (seasonal and extended time scale). For the first time, IMD used the Monsoon Mission dynamical model to prepare operational seasonal forecast of 2017 monsoon rainfall over India.
- The Ministry has now launched the Monsoon Mission Phase II program (2017-2020) with emphasis on predicting extremes and development of applications based on monsoon forecasts.
SAFAR
- SAFAR stands for System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research
- It is a research program to build Air-Pollution mitigation strategies in consonance with nation’s economic development
- It is launched in greater metropolitan cities of India to provide location specific information on air quality in near real time
- It has been combined with the early warning system on weather parameters
- The ultimate objective of the project is to increase awareness among general public regarding the air quality in their city well in advance so that appropriate mitigation measures and systematic action can be taken up for betterment of air quality and related health issues.
- SAFAR was developed indigenously by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune and operationalized by India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Pollutants monitored: PM1, PM2.5, PM10, Ozone, CO, NOx (NO, NO2), SO2, BC, Methane (CH4), Non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), VOC’s, Benzene, Mercury.
- Monitored Meteorological Parameters: UV Radiation, Rainfall, Temperature, Humidity, Wind speed, Wind direction etc.
Ministry Of Food Processing Industries
Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana

- Earlier named as SAMPADA (Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters), this central sector scheme has been approved for the period of 2016-20 coterminous with the 14th Finance Commission cycle.
- It is an umbrella scheme incorporating ongoing schemes of the Ministry of Food Processing which will result in creation of modern infrastructure with efficient supply chain management from farm gate to retail outlet.
Schemes under PMKSY
- Mega Food Parks
- Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure
- Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure
- Creation/Expansion of Food Processing & Preservation Capacities
- Infrastructure for Agro-processing Clusters
- Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages
- Human Resources and Institutions.
Mega Food Parks Scheme
- Mega Food Parks Scheme launched by the government in 2008 provides financial assistance upto 50 crores to setup modern infrastructure facilities for food processing called Mega Food Parks.
- It establishes a mechanism to bring together farmers, processors and retailers and link agriculture production to the market so as to ensure maximization of value addition, minimization of wastage and improving farmers’ income.
- The primary objective of the Scheme is to provide modern infrastructure facilities for the food processing along the value chain from the farm to the market with a cluster based approach based on a hub and spokes model.
- It includes the creation of infrastructure for primary processing and storage near the farm in the form of Primary Processing Centres (PPCs) and Collection Centres (CCs) and common facilities and enabling infrastructure like roads, electricity, water, ETP facilities etc. at Central Processing Centre (CPC). These PPCs and CCs act as aggregation and storage points to feed raw material to the food processing units located in the CPC.
Integrated Cold Chain Projects
- The objective of the scheme for Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure of Ministry of Food Processing Industries is to provide integrated cold chain, preservation and value addition infrastructure facilities without any break, from the farm gate to the consumer in order to reduce post-harvest losses of horticulture and non-horticulture agri-produce.
- This will enable linking groups of producers to processors and market through a well-equipped supply chain and cold chain, thereby ensuring remunerative prices to farmers and year-round availability of food products to consumers.
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries is implementing the Central Sector Scheme for Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure,wherein financial assistance in the form of grant-in-aid upto maximum of Rs. 10 crore per project is provided for setting up the cold chain infrastructure in the country.
Nivesh Bandhu
- It is an investor facilitation portal which would provide information on Central and State Governments’ investor friendly policies, agro-producing clusters, infrastructure, and potential areas of investment in the food processing sector.
Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
FAME India Scheme
- The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 was unveiled in 2013as part of the scheme FAME-India [Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles in India].
- The scheme is being implemented over a period of 6 years till 2020.It will support the hybrid and electric vehicles market development and its manufacturing eco-system to achieve self-sustenance at the end of this period. Government of India is committed to instil confidence in the industry and allow them to plan required investments and create needed capacities.
- This will also enable the scheme to align with Government’s Make in India initiative. The scheme focuses on four areas:Technology Development,Demand Creation,Pilot Projects,Charging Infrastructure.
- The scheme is one of the green initiatives of the Government of India, which will be one of the biggest contributors in reducing pollution from road transport sector in the near future. This scheme is aimed at incentivizing all vehicle segments like 2-Wheelers, 3-Wheelers, 4-Wheeler Vehicles, Light Commercial Vehicles and Buses.
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan
- Government of India launched the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020 in 2013. It aims to achieve national fuel security by promoting hybrid and electric vehicles in the country.
- There is an ambitious target to achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and electric vehicles year on year from 2020 onwards.
- Government aims to provide fiscal and monetary incentives to kick start this nascent technology. With the support from the Government, the cumulative sale is expected to reach 15-16 Million by 2020. It is expected to save 9500 Million Liters of crude oil equivalent to Rs. 62000 Cr. savings.
Ministry Of Home Affairs
Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems
- The Crime and Criminal Tracking Network Systems (CCTNS) was conceptualized by the Ministry of Home Affairs in detailed consultation with all stakeholders and is being implemented as a “Mission Mode Project (MMP)” since 2009.
- CCTNS aims at creating a comprehensive and integrated system for enhancing the efficiency and effective policing at all levels and especially at the Police Station level through adoption of principles of e-Governance, and creation of a nationwide networked infrastructure for evolution of IT-enabled state of- the-art tracking system around “investigation of crime and detection of criminals” in real time, which is a critical requirement in the context of the present day internal security scenario.
- Digital Police Portal has been launched under the CCTNS project: It will enable citizens to register FIRs online and the portal will initially offer seven Public Delivery Services in 34 States & UTs, like Person and Address Verification e.g. of employees, tenants, nurses etc, permission for hosting Public Events, Lost & Found Articles and Vehicle theft etc.
- The Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) aims to integrate the CCTNS project with the e-courts and e-prisons databases in the first instance and with the other pillars of the criminal justice system – Forensics, Prosecution, Juvenile homes and a nationwide Fingerprint data base of criminals in a phased manner.
UDAAN
- It is a Special Industry Initiative for J&K funded by Ministry of Home Affairs and implemented by National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC).
- It is focused on providing skills and job opportunities to youth of Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) who are graduate, post graduate and three year diploma engineers. Simultaneously, the aim is also to provide exposure to corporate India towards the rich talent pool available in J&K.
‘Bharat Ke Veer
- It is an IT based platform, with an objective to enable willing donors to contribute towards the family of a braveheart who sacrificed his/her life in line of duty. The amount so donated will be credited to the account of ‘Next of Kin’ of those Central Armed Police Force/Central Para Military Force soldiers.
Modernisation of Police Forces (MPF)
- Cabinet has given its approval for implementation of umbrella scheme of “Modernisation of Police Forces (MPF)” for years 2017-18 to 2019-20.
- Special provision has been made under the Scheme for internal security, law and order, women security, availability of modern weapons, mobility of police forces, logistics support, hiring of helicopters, upgradation of police wireless, National Satellite Network, CCTNS project, E-prison project etc.
- Under the umbrella scheme, central budget outlay of Rs.10,132 crore has been earmarked for internal security related expenditure for Jammu & Kashmir, North Eastern States and left wing extremism affected States.
- Scheme of Special Central Assistance (SCA) for 35 worst LWE affected districts has been introduced with an outlay of Rs.3,000 crore to tackle the issue of underdevelopment in these district
Ministry of Labour and Employment
Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay Shramev Jayate Karyakram
Key elements:
- A dedicated Shram Suvidha Portal: That would allot Labour Identification Number (LIN) to nearly 6 lakhs units and allow them to file online compliance for 16 out of 44 labour laws
- An all-new Random Inspection Scheme: Utilizing technology to eliminate human discretion in selection of units for Inspection, and uploading of Inspection Reports within 72 hours of inspection mandatory
- Universal Account Number: Enables 4.17 crore employees to have their Provident Fund account portable, hassle-free and universally accessible
- Apprentice Protsahan Yojana: Will support manufacturing units mainly and other establishments by reimbursing 50% of the stipend paid to apprentices during first two years of their training
- Revamped Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana: Introducing a Smart Card for the workers in the unorganized sector seeded with details of two more social security schemes
Shram Suvidha Portal:
- The objective of the unified web portal is to consolidate information of Labour Inspection and its enforcement, which will lead to transparency and accountability in inspections. The compliances would be reportable in Single Harmonized Form which will make it simple and easy for those filing such forms. The performance will be monitored using key indicators thus making the evaluation process objective. The portal also has an effective grievance redressal System. It promotes the use of a common Labour Identification Number (LIN) by all implementing agencies.
The 4 main features of the portal are:
- Unique labour identification number (LIN) will be allotted to Units to facilitate online registration.
- Filing of self-certified and simplified Single Online Return by the industry. Now Units will only file a single consolidated Return online instead of filing 16 separate Returns.
- Mandatory uploading of inspection Reports within 72 hours by the Labour inspectors.
- Timely redressal of grievances will be ensured with the help of the portal.
Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana
- The Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY) is a scheme to incentivise employers registered with the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) for job creation by the Government paying the 8.33% contribution of employers to the Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) in respect of new employees having a new Universal Account Number (UAN). For the textile (apparel) sector, the Government will also be paying the 3.67% Employees Provident Fund (EPF) contribution of the eligible employer for these new employees.
- This Scheme has a dual benefit, where, on the one hand, the employer is incentivised for increasing the employment base of workers in the establishment, and on the other hand, a large number of workers will find jobs in such establishments. A direct benefit is that these workers will have access to social security benefits of the organized sector.
- Scope of the scheme has been enhanced recently – The GoI will now contribute the employer’s full admissible contribution (12%) for the first three years from the date of registration of the new employee, and for all the sectors including existing beneficiaries for their remaining period of three years.
Rehabilitation of Bonded Labourers scheme
- It provides financial assistance for rehabilitation of a rescued bonded labour.
- ₹1 lakh per adult male beneficiary
- ₹2 lakh for special category beneficiaries such as women and children
- ₹3 lakh in cases of extreme deprivation or marginalisation such as transgenders, women or children rescued from ostensible sexual exploitation or trafficking, in cases of differently abled persons, or in situations where the district magistrate deems it fit.
- It provides for creation of a Bonded Labour Rehabilitation Fund at District level by each State with a permanent corpus of at least Rs. 10 lakh.
- The entire penalties recovered from the perpetuators of the bonded labour upon conviction, may be deposited in this special fund. This fund will be utilised for extending immediate help to the released bonded labourers
PENCIL Portal
- It is an electronic portal to combat the menace of child labour and trafficking.
- It has various components – complaint corner, child & adolescent labour tracking system, NCLP (National Child Labour Project) and State Resource Centre.
- At the State Government level the monitoring is to be done by State Resource Centre established at State Labour Department. At district level District Nodal Officers (DNOs) are nominated to take action on the complaints of their respective districts.
National Child Labour Project (NCLP) Scheme
- The scheme was started to rehabilitate child labour by adopting a sequential approach.
- Under the scheme the children engaged in child labour would be identified and withdrawn from the identified areas.
- They are then prepared for mainstream education along with vocational training and ensure convergence of services for the benefit of child and family.
- The Scheme will be implemented in close coordination with state, district administration and civil society.
National Career Service
- It was launched in 2017 to replace the National Employment Service comprising a network of 978 employment exchanges.
- IT comprises an ICT-based portal, a countrywide set-up of career centres, a multilingual call centre, and a network of career counsellors.
- The national ICT portal primarily facilitates registration of job seekers, job providers, skill providers, career counsellors etc.
- It envisages 100 model career centres to provide a variety of employment related services with primary focus on Career Counseling.
Revised Integrated Housing Scheme, 2016
- Revised Integrated Housing Scheme for workers is being implemented by the Ministry of Labour and The Revised Integrated Housing Scheme (RIHS), 2016 has been launched for workers.
- The scheme provides housing subsidy of Rs. 1,50,000/- per worker for construction of house to be paid in three installments directly into the bank account of the beneficiaries. The installments shall be released in the slab of 25% (advance), 60% (After lintel level) and 15% (after completion).
- Land area shall not less than 60s sq.meter for general category. However plot of smaller area/size can be considered in case of Economically Weaker Sections (EWS), Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes provided the standards and specifications laid down in Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana are broadly followed.
- No deposit is required to be made by the beneficiary for release of subsidy. There shall also be no cost ceiling in terms of the construction cost.The construction of the house is to be completed by 18 months.
Ministry of Law and Justice
Pro Bono Legal Service
- The initiative is a web based platform, through which interested lawyers can register themselves to volunteer pro bono services for the underprivileged litigants.
- It aims to create a database capturing vital information of lawyers for appropriate positions in the relevant field.
NYAYA Mitra
- Nyaya Mitra would be a retired judicial or executive officer (with legal experience). Function of Nyaya Mitra
- The scheme is intended to facilitate the connection of litigants to District Legal Service Authority (DLSA), CSC Tele Law, and other government agencies and civil society organisations,Render assistance towards prison reforms.
Access to Justice for Marginalised People
- The project involves awareness campaign, capacity building and action directed toward strengthening access to justice for the poor, particularly women, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and minorities.
- It is in partnership of United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the Department of Justice (DoJ).
- The project extends to the eight UN Development Action Framework states of Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Odisha.
- Its main components are: Strengthening Capacities of Legal Services Authorities, Technical Support to National Mission on Justice Delivery and Legal Reforms, Legal Empowerment and Fresh Evidence Gathered to Strengthen Policy on Judicial Training and Justice Delivery.
Legal Information Management & Briefing System (LIMBS)
- It aims to have information relating to all court/tribunal cases being handled by the various Ministries/Departments and other organs of the Government of India will be available on a single web-based online application.
- Government will intervene and give legal opinion online to resolve such disputes.
Tele-Law Initiative
- It is a portal launched to make legal aid easily accessible to the marginalized communities and citizens living in rural areas.
- It will be available across the CSC network. It will enable people to seek legal advice from lawyers through video conferencing.
- Every CSC will engage a Para Legal Volunteer (PLV), who will be the first point of contact for the rural citizens.
Ministry of Mines
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY)
- This programme meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations. The most productive mining areas in the country are largely areas inhabited by scheduled tribes.
- They also are mainly located in the areas covered by the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution. The PMKKKY is, therefore, very sharply focused on safeguarding the health, environment and economic conditions of the tribals and providing them with opportunities to benefit from the vast mineral resources that are extracted from the areas where they live.
- The Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY) will be implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) of the respective districts using the funds accruing to the DMF.
- The Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Amendment Act, 2015, mandated the setting up of District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) in all districts in the country affected by mining related operations. The Central Government has notified the rates of contribution payable by miners to the DMFs.
TAMRA (Transparency, Auction Monitoring and Resource Augmentation)
- With an objective to enhance transparency and accountability as a part of the Ease of Doing Business in the Mining sector, TAMRA (Transparency, Auction Monitoring and Resource Augmentation) portal and Mobile Application was launched.
- Ministers of Mining and senior officers from 12 mineral rich States would also be connected through videoconferencing.
- TAMRA will be an interactive platform for all the stakeholders to compress the timelines for statutory and other clearances as it would help minimize the gestation period for commencing production.
- Further, TAMRA covers block-wise, state-wise and mineral-wise information of the blocks to be auctioned, monitors various statutory clearances, and also highlights the additional resources generated through e-Auction.
- In case of delay in obtaining any clearances, TAMRA will send triggers to the concerned authority so that the remedial steps can be taken immediately by those responsible.
- The Ministry of Mines will also receive triggers generated by TAMRA and will facilitate in expediting clearances. This portal also enables successful bidder to give suggestions/inputs.
Project “Sudoor Drishti”
- Indian Bureau of Mines has signed a MoU with National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), ISRO to undertake a pilot project on “monitoring of mining activities using satellite imagery and capacity building of IBM officers for three years including technical support for setting up of remote sensing laboratory in IBM”.
- Two Remote Sensing Labs are being set up at Hyderabad and Nagpur.
Mining Surveillance System (MSS)
- Mining Surveillance System (MSS) is a satellite-based monitoring system which aims to establish a regime of responsive mineral administration by curbing instances of illegal mining activity through automatic remote sensing detection technology.
- Ministry of Mines & Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM) have developed the MSS, with assistance from Bhaskaracharya Institute for space applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG), Gandhinagar and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY).
- The system works on the basic premise that most minerals occur in the continuity and their occurrence is not limited to the lease area but is likely to extend in the vicinity. The MSS checks a region of 500 meters around the existing mining lease boundary to search for any unusual activity which is likely to be illegal mining. Any discrepancy is found is flagged-off as a trigger.
- The MSS is a transparent & bias-free system, having a quicker response time and capability of effective follow-up. The deterrence effect of ‘Eyes watching from the Sky’ would be extremely fruitful in curbing instances of illegal mining.
- A user friendly mobile app for MSS has been created and launched for enabling public participation in assisting the governments endeavour to curb illegal mining, which was being used by the inspecting officials to submit compliance reports of their inspections.
Star Rating of Mines
- Ministry of Mines, in its endeavor for taking up exhaustive and universal implementation of the Sustainable Development Framework (SDF) in mining, has evolved a system of Star Rating of Mines.
- The Ministry of Mines instituted the Sustainable Development Framework (SDF) for taking up mining activity, encompassing inclusive growth, without adversely affecting the social, economic and environmental well-being, at present and also in future generation.
- It has been institute as a two tier system providing self-evaluation templates to be filled in by the mine operator followed by validation through Indian Bureau of Mines.
- Based on the performance of the mining lease, 1 to 5 star rating, the positive impact of getting higher Star Rating will drive miners to quickly adopt sustainable mining practices.
- The Star Rating has been included as statutory provision in the MCDR for time- bound (2 years) achieving of minimum 4 stars.
- A web enabled online system for evaluation of measures has been developed and launched.













