Ministry of Health & Family Welfare – Part 2
Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY)

- The Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY) was announced in 2003 with objectives of correcting regional imbalances in the availability of affordable/ reliable tertiary healthcare services and also to augment facilities for quality medical education in the country.
- It is a central sector scheme.
- PMSSY has two components:
- (i) Setting up of AIIMS like Institutions
- (ii) Upgradation of Government Medical College Institutions.
- Setting up of new AIIMS would not only transform health education and training but also address the shortfall of health care professionals in the region. Construction of new AIIMS is fully funded by the Central Government. The Operations & Maintenance expenses on new AIIMS are also fully borne by the Central Government.
Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK)

- Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK) is a new initiative aiming at early identification and early intervention for children from birth to 18 years to cover 4 ‘D’s viz. Defects at birth, Deficiencies, Diseases, Development delays including
- It is important to note that the 0 – 6 years age group will be specifically managed at District Early Intervention Center ( DEIC ) level while for 6 -18 years age group, management of conditions will be done through existing public health facilities. DEIC will act as referral linkages for both the age groups.
- First level of screening is to be done at all delivery points through existing Medical Officers, Staff Nurses and ANMs. After 48 hours till 6 weeks the screening of newborns will be done by ASHA at home as a part of HBNC package. Outreach screening will be done by dedicated mobile block level teams for 6 weeks to 6 years at anganwadis centres and 6 – 18 years children at school.
- Once the child is screened and referred from any of these points of identification, it would be ensured that the necessary treatment/intervention is delivered at zero cost to the family.
- The services aim to cover children of 0 -6 years of age in rural areas and urban slums in addition to children enrolled in classes I to XII in Government and Government aided It is expected that these services will reach to about 27 crores children in a phased manner.
Rashtriya Kishor Swasthya Karyakram (RKSK)

- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare has launched a health programme for adolescents, in the age group of 10-19 years, which would target their nutrition, reproductive health and substance abuse, among other issues.
- Objectives include:
- Reduce the prevalence of malnutrition among adolescent girls and boys
- Reduce the prevalence of iron-deficiency anaemia (IDA) among adolescent girls and boys
- Improve knowledge, attitudes and behaviour, in relation to sexual and reproductive health,Reduce teenage pregnancies,Improve birth preparedness, complication readiness and provide early parenting support for adolescent parents
- Address mental health concerns of adolescents, increase adolescents’ awareness of the adverse effects and consequences of substance misuse
- Promote behaviour change in adolescents to prevent NCDs such as hypertension, stroke, cardio-vascular diseases and diabetes
National Viral Hepatitis Surveillance Programme

- Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by one of the five hepatitis viruses, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E. The Government of India through the National Centre for Disease Control is implementing the National Viral Hepatitis Surveillance Programme.
- Objectives include:
- To establish laboratory network for laboratory based surveillance of viral hepatitis in different geographical locations of India.
- To ascertain the prevalence of different types of viral hepatitis in different zones of the country.
- To provide laboratory support for outbreak investigation of hepatitis through established network of laboratories.
- To develop technical material for generating awareness among healthcare providers and in the community about waterborne and blood borne hepatitis.
India Newborn Action Plan
- India Newborn Action Plan (INAP) was launched in September 2014, for accelerating the reduction of preventable newborn deaths and stillbirths in the country – with the goal of attaining ‘Single Digit Neo-natal Mortality Rate (NMR) by 2030’ and ‘Single Digit Still Birth Rate (SBR) by 2030’.
- Currently, there are estimated 47 lakh neonatal deaths annually.The neo-natal deaths are expected to reduce to below 2.28 lakh annually by 2030, once the goal is achieved.
Ayushman Bharat–PM Jan Arogya Yojana

- Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme having central sector component under Ayushman Bharat Mission anchored in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW). It is an umbrella of two major health initiatives, namely Health and wellness Centres and National Health Protection Scheme.
- Health and Wellness Centres: Under this 1.5 lakh existing sub centres will bring health care system closer to the homes of people in the form of Health and wellness centres. These centres will provide comprehensive health care, including for non-communicable diseases and maternal and child health services.
List of Services to be provided at Health & Wellness Centre
- Pregnancy care and maternal health services
- Neonatal and infant health services
- Child health
- Chronic communicable diseases
- Non-communicable diseases
- Management of mental illness
- Dental care
- Eye care
- Geriatric care Emergency medicine
National Health Protection Mission (AB-PMJAY)

- AB-PMJAY provides a defined benefit cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family per year. This cover will take care of almost all secondary care and most of tertiary care procedures.
- To ensure that nobody is left out (especially women, children and elderly) there will be no cap on family size and age in the scheme.
- The benefit cover will also include pre and post-hospitalisation expenses. All pre-existing conditions will be covered from day one of the policy. A defined transport allowance per hospitalization will also be paid to the beneficiary.
- Benefits of the scheme are portable across the country and a beneficiary covered under the scheme will be allowed to take cashless benefits from any public/private empanelled hospitals across the country.
- The beneficiaries can avail benefits in both public and empanelled private facilities.
- To control costs, the payments for treatment will be done on package rate (to be defined by the Government in advance) basi For beneficiaries, it will be a cashless, paper less transaction. Keeping in view the State specific requirements, States/ UTs will have the flexibility to modify these rates within a limited bandwidth.
National Programme for the Health Care for the Elderly

- The National Programme for the Health Care for the Elderly (NPHCE) is an articulation of the International and national commitments of the Government as envisaged under the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP) adopted by the Government of India in 1999 & Section 20 of “The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007” dealing with provisions for medical care of Senior Citizen.
Objectives include:
- To provide an easy access to promotional, preventive, curative and rehabilitative services to the elderly through community based primary health care approach
- To identify health problems in the elderly and provide appropriate health interventions in the community with a strong referral backup support.
- To build capacity of the medical and paramedical professionals as well as the care-takers within the family for providing health care to the elderly.
- To provide referral services to the elderly patients through district hospitals, regional medical institutions
- Convergence with National Rural Health Mission, AYUSH and other line departments like Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
National AIDS control programme

- The National AIDS Control Programme (NACP), launched in 1992, is being implemented as a comprehensive programme for prevention and control of HIV/ AIDS in India. Over time, the focus has shifted from raising awareness to behaviour change, from a national response to a more decentralized response and to increasing involvement of NGOs and networks of People living with HIV (PLHIV).
- The HIV Estimations 2017 is the 14th round in the series of HIV Estimations under National AIDS Control Programme (NACP). NACO undertakes HIV estimations biennially in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) – National Institute of Medical Statistics (NIMS). The first round of HIV estimation in India was done in 1998, while the last round was done in 2015.
- The report highlights the significant achievement of National AIDS response on prevention as well as on treatment front but has also indicated that there is no place for complacency as country move forward on ambitious goal of attaining the ‘End of AIDS’ by 2030.
- The report concludes that, overall, the impact of the programme has been significant with more than 80% decline in estimated new infection from peak of epidemic in 1995. Similarly, estimated AIDS related death declined by 71% since its peak in 2005.
National Leprosy Eradication Programme

- The National Leprosy Eradication Programme is a centrally sponsored Health Scheme of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India.
- While the NLEP strategies and plans are formulated centrally, the programme is implemented by the States/UTs. The Programmes also supported as Partners by the World Health Organization, The International Federation of Anti-leprosy Associations (ILEP) and few other Non-Govt. Organizations.
- The country was declared leprosy-free on December 31, 2005
- 34 states and UTs achieved elimination out of 36 States/ UTs.
- Only the state of Chhattisgarh and the UT of Dadra & Nagar Haveli were yet to achieve elimination.
- In 2005 India achieved the goal of elimination of leprosy, defined as less than 1 case per 10,000 populations.
- The SPARSH Leprosy Awareness Campaign (SLAC) was launched to promote awareness and address the issues of stigma and discrimination.
- Recently government enacted Personal Law Bills 2018 amendment to remove leprosy as a ground for divorce or separation.
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme
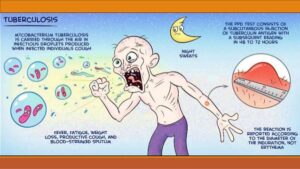
- The National TB Control Programme was started in 1962 with the aim to detect cases earliest and treat them. In the district, the programme is implemented through the district Tuberculosis Centre (DTC) and the Primary Health Institutions.
- The Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP), based on the Directly Observed Treatment, Short Course (DOTS) strategy, began as a pilot project in 1993 and was launched as a national programme in 1997 but rapid RNTCP expansion began in late 1998. The nation-wide coverage was achieved in 2006.
- National Strategic Plan for 2017- 25 for TB elimination in India: The NSP 2017 – 2025 builds on the success and learnings of the last NSP and encapsulates the bold and innovative steps required to eliminate TB in India by 2030.
- It is crafted in line with other health sector strategies and global efforts, such as the draft National Health Policy 2015, World Health Organization’s (WHO) End TB Strategy, and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations (UN).
Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment
- With the aim to reduce the expenditure incurred by patients on treatment of cancer and heart diseases, the Ministry for Health & Family Welfare, has launched the Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) programme.
- As part of the programme, retail outlets will sell drugs for the cancer and heart diseases at highly discounted rates.
- The AMRIT pharmacy would be selling 202 cancer and 186 cardio-vascular drugs, and 148 types of cardiac implants at very affordable prices. Patients can buy medicines and implants at 50 to 60 percent cheaper prices than the open market from AMRIT outlet.













