UPSC Mains – International Relations – United Nations :Article Analysis
by
Mentors4ias
·
March 1, 2019
United Nations: Article Analysis

Mains Topic: GS-2
International Relations
Introduction
- Headquartered in New York, USA, The United Nations is a unique organization of independent countries designed to make the enforcement of international law, security, economic development, social progress and human rights easier for countries around the world.
- The organisation formally (officially) came into existence on 24th October 1945, with 51 countries considered as founding members and several non-governmental organisation, who signed the charter which was drafted at the UN Conference on International Organisation in San Francisco, California.
- By the end of July 2011, the membership of the UN had grown to 193 as the South Sudan is being welcomed as the last member into the community of nations on 14th July 2011.
The Evolution of UN
- The First World War encouraged the world to invest in an international organisation to deal with conflict. Many believed that such an organisation would help the world to avoid war. As a result, the League of Nations was born. However, despite its initial success, it could not prevent the Second World War (1939-45). Many more people died and were wounded in this war than ever before.
- The UN was founded as a successor to the League of Nations. It was established in 1945 immediately after the Second World War. The organisation was set up through the signing of the United Nations Charter by 51 states.
- It tried to achieve what the League could not between the two world wars. The UN’s objective is to prevent international conflict and to facilitate cooperation among states.
- It was founded with the hope that it would act to stop the conflicts between states escalating into war and, if war broke out, to limit the extent of hostilities. Furthermore, since conflicts often arose from the lack of social and economic development, the UN was intended to bring countries together to improve the prospects of social and economic development all over the world.
- In the UN General Assembly, all members have one vote each. In the UN Security Council, there are five permanent members. These are: the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France and China.
- These states were selected as permanent members as they were the most powerful immediately after the Second World War and because they constituted the victors in the War.
UN Agencies
- The UN consists of many different structures and agencies. War and peace and differences between member states are discussed in the General Assembly as well as the Security Council.
- Social and economic issues are dealt with by many agencies including the World Health Organisation (WHO), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the United Nations Human Rights Commision (UNHRC), the United Nations High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR), the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), and the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), among others.
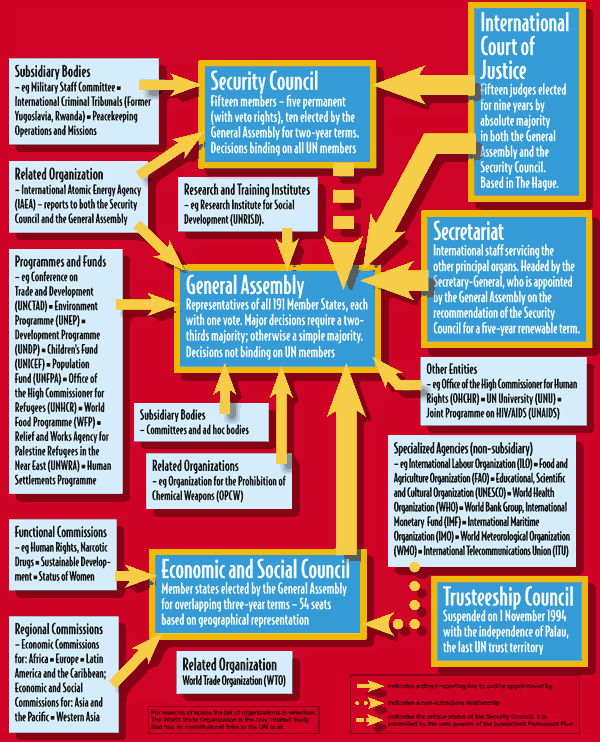
Main Organs of the UN
General Assembly:
- The General Assembly is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the UN. All 193 Member States of the UN are represented in the General Assembly, making it the only UN body with universal representation.
Security Council:
- The Security Council has primary responsibility, under the UN Charter, for the maintenance of international peace and security. It has 15 Members (5 permanent and 10 non-permanent members). Each Member has one vote. The Security Council takes the lead in determining the existence of a threat to the peace or act of aggression.
- In some cases, the Security Council can resort to imposing sanctions or even authorize the use of force to maintain or restore international peace and security.
Economic and Social Council
- The Economic and Social Council is the principal body for coordination, policy review, policy dialogue and recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues, as well as implementation of internationally agreed development goals.
International Court of Justice
- The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations. Its seat is at the Peace Palace in the Hague (Netherlands). The Court’s role is to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
Secretariat
- The Secretariat comprises the Secretary-General and tens of thousands of international UN staff members who carry out the day-to-day work of the UN as mandated by the General Assembly and the Organization’s other principal organs.
- The Secretary-General is chief administrative officer of the Organization, appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a five-year, renewable term.
FUNCTIONS OF THE UNITED NATIONS:
Maintain peace an d security
- The main function of the UN is to maintain peace and security of all of its member states. The UN does this by working to prevent conflict; helping parties in conflict to make peace; peacekeeping; and creating the conditions to allow peace to hold & flourish. These activities often overlap and should reinforce one another, to be effective.
Protect Human Rights
- The term Human Right is mentioned in the founding charter of UN making the promotion and protection of human rights a key purpose and guiding principle of the Organization.
- In 1948, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights brought human rights into the realm of international law. Since then, the Organization has diligently protected human rights through legal instruments and on-the-ground activities.
- The Office of UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) supports the human rights components of peacekeeping missions in several countries with many regional offices in several countries.
Deliver Humanitarian Aid
- The term is mentioned in its charter “to achieve international co-operation in solving international problems of an economic, social, cultural, or humanitarian character.”
- Four UN entities, the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), the United Nations Refugee Agency (UNHCR), the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and the World Food Program (WFP) have primary roles in the delivery of relief assistance.
Promote Sustainable Development
- The main UN offices involved in this are UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, The UN Development Program, UN offices for Disaster Risk Reduction, Sandai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 and many agencies like World Health Organisation, The Food and Agriculture Organization, UNICEF, UNESCO and the UN Environment Program.
Uphold International Laws
- The UN Charter, in its Preamble, set an objective: “to establish conditions under which justice and respect for the obligations arising from treaties and other sources of international law can be maintained”.
- Ever since, the development of, and respect for international law has been a key part of the work of the Organization.
Reform Of The UN After The Cold War:
- In recent years, there have been demands for reform of the world body. However, there is little clarity and consensus on the nature of reform.
- Two basic kinds of reforms face the UN: reform of the organisation’s structures and processes; and a review of the issues that fall within the jurisdiction of the organisation. Almost everyone is agreed that both aspects of reform are
- What they cannot agree on is precisely what is to be done, how it is to be done, and when it is to be done.
- Major reform imperative is the UN’s governance, starting with the Security Council, the composition of which no longer reflects global geopolitical realities.
- The Charter gave the permanent members a privileged position to bring about stability in the world after the Second World War. The main privileges of the five permanent members are permanency and the veto power. The non-permanent members serve for only two years at a time and give way after that period to newly elected members. A country cannot be re-elected immediately after completing a term of two years. The non-permanent members are elected in a manner so that they represent all continents of the world.
- Indeed, the Western Europe and Other Group now accounts for three of the five permanent members (France, the United Kingdom, and the US).
- That leaves only one permanent position for the Eastern European Group (Russia), one for the Asia-Pacific Group (China), and none for Africa or Latin America. There should reformation of Security Council, or else it will make UN not functioning very well. The UN can function much better if the big powers do not intervene in various issues to protect their vested interests.
- The rotating seats on the Security Council do not adequately restore regional balance. Even with two of the ten rotating Security Council seats, the Asia-Pacific region is still massively under-represented.
- The Asia-Pacific region accounts for roughly 55% of the world’s population and 44% of its annual income but has just 20% (three out of 15) of the seats on the Security Council.
- Asia’s inadequate representation poses a serious threat to the UN’s legitimacy, which will only increase as the world’s most dynamic and populous region assumes an increasingly important global role.
- One possible way to resolve the problem would be to add at least four Asian seats: one permanent seat for India, one shared by Japan and South Korea (perhaps in a two-year, one-year rotation), one for the ASEAN countries (representing the group as a single constituency), and a fourth rotating among the other Asian countries.
- The present Security Council and other agencies of UN’s global governance are undemocratic in structure.
- If the UN should continue to fulfill its unique and vital global role in the twenty-first century, it needs a multi-level upgradation. The UN should be made fit for the new age of sustainable development.
- In order to strengthen the role of the United Nations, efforts should be made to uphold the purposes and principles of the Charter of the United Nations. Role of the United Nations in area of development should be strengthened.
- All the Member States of the United Nations should get the right of equal participation in international affairs and the interests of the developing countries should be safeguarded.
- UN also needs cooperation from the member states. There are many cases in which the member nations have violated the rules and regulations of the UN. This is not in particular to any specific nation. Many nations are acting against the norms of international society. China’s position on South China Sea dispute is an example.
INDIA AND THE U.N REFORMS
- India has supported the restructuring of the UN on several grounds. It believes that a strengthened and revitalised UN is desirable in a changing world. India also supports an enhanced role for the UN in promoting development and cooperation among states. India believes that development should be central to the UN’s agenda as it is a vital precondition for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- One of India’s major concerns has been the composition of the Security Council, which has remained largely static while the UN General Assembly membership has expanded considerably.
- India considers that this has harmed the representative character of the Security Council. It also argues that an expanded Council, with more representation, will enjoy greater support in the world community.
- We should keep in mind that the membership of the UN Security Council was expanded from 11 to 15 in 1965. But, there was no change in the number of permanent members.
- Since then, the size of the Council has remained stationary. The fact remains that the overwhelming majority of the UN General Assembly members now are developing countries. Therefore, India argues that they should also have a role in shaping the decisions in the Security Council which affect them.
- India supports an increase in the number of both permanent and non-permanent members. Its representatives have argued that the activities of the Security Council have greatly expanded in the past few years.
- The success of the Security Council’s actions depends upon the political support of the international community. Any plan for restructuring of the Security Council should, therefore, be broad-based. For example, the Security Council should have more developing countries in it.
- India itself also wishes to be a permanent member in a restructured UN.
Why India should be a permanent member in the Security Council
- India is the second most populous country in the world comprising almost one-fifth of the world population.
- Moreover, India is also the world’s largest democracy. India has participated in virtually all of the initiatives of the UN.
- Its role in the UN’s peacekeeping efforts is a long and substantial one. The country’s economic emergence on the world stage is another factor that perhaps justifies India’s claim to a permanent seat in the Security Council.
- India has also made regular financial contributions to the UN and never faltered on its payments. India is aware that permanent membership of the Security Council also has symbolic importance. It signifies a country’s growing importance in world affairs.
- This greater status is an advantage to a country in the conduct of its foreign policy: the reputation for being powerful makes you more influential.
- Despite India’s wish to be a permanent veto-wielding member of the UN, some countries question its inclusion. Neighbouring Pakistan, with which India has troubled relations, is not the only country that is reluctant to see India become a permanent veto member of the Security Council.
- Some countries, for instance, are concerned about India’s nuclear weapons capabilities. Others think that its difficulties with Pakistan will make India ineffective as a permanent member.
- Yet others feel that if India is included, then other emerging powers will have to be accommodated such as Brazil, Germany, Japan, perhaps even South Africa, whom they oppose.
- There are those who feel that Africa and South America must be represented in any expansion of the permanent membership since those are the only continents not to have representation in the present structure.
- Given these concerns, it may not be very easy for India or anyone else to become a permanent member of the UN in the near future
Source: New Internationalist, NCERT and UN


















